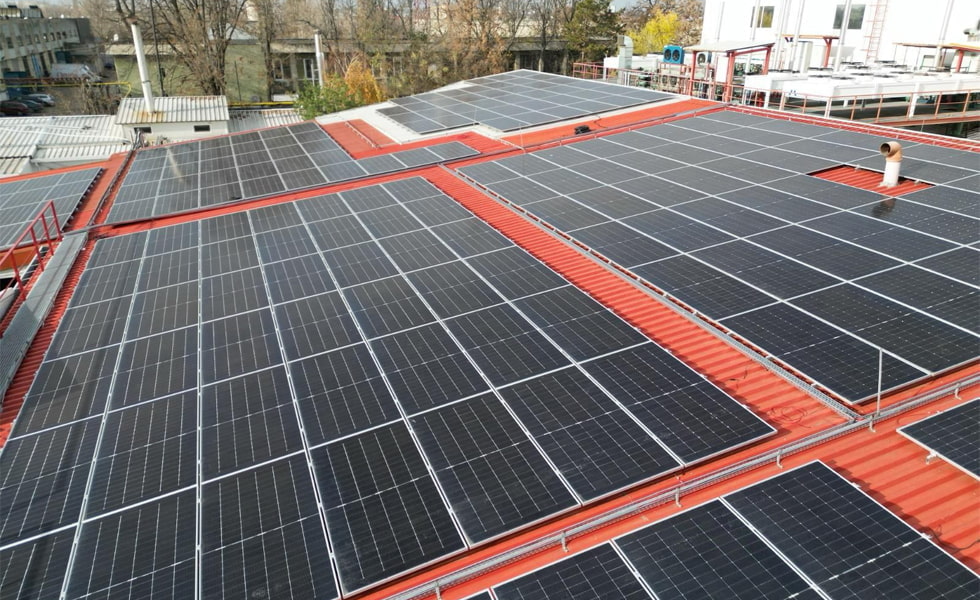
1. El mercado del "PIB fotovoltaico" se concentra principalmente en los países en desarrollo
1.1. Demanda del mercado e impulso de crecimiento
Los países en desarrollo que se encuentran en una etapa de rápido crecimiento económico tienen una demanda creciente de electricidad. Sin embargo, los métodos tradicionales de suministro de energía a menudo no pueden satisfacer esta demanda en rápido crecimiento y van acompañados del doble desafío de la contaminación ambiental y la seguridad energética. La industria fotovoltaica, con sus características limpias y renovables, se ha convertido en una opción importante para que estos países resuelvan problemas energéticos y promuevan el crecimiento económico.
Tomemos a la India como ejemplo. Como segundo país más poblado del mundo, la demanda de electricidad de la India es enorme y continúa creciendo. Sin embargo, desde hace mucho tiempo, la India sufre una grave escasez de suministro eléctrico, especialmente en las zonas remotas y rurales. Según datos del gobierno indio, India tiene más de 90 millones de personas sin electricidad y cientos de millones de personas carecen de electricidad.
El desarrollo de una generación de energía fotovoltaica barata y convenienteproporciona a la India una forma eficaz de resolver el problema de la escasez de energía.
En los últimos años, el gobierno indio ha otorgado gran importancia al desarrollo de la industria fotovoltaica y ha introducido una serie de políticas alentadoras, que incluyen contratos de compra de energía a largo plazo, incentivos fiscales y subsidios. Estas políticas han estimulado enormemente la vitalidad del mercado y promovido el rápido crecimiento del mercado fotovoltaico.
Las estadísticas muestran que en el primer semestre de 2024, la nueva capacidad instalada fotovoltaica de la India alcanzó los 14,9 GW, un aumento interanual del 282 %, superando toda la capacidad instalada del primer semestre anterior. Entre ellos, la capacidad instalada fotovoltaica en tejados de la India aumentó en 1,1 GW, un incremento interanual del 26%.
En agosto de 2024, la capacidad instalada fotovoltaica total de la India alcanzó los 89,43 GW, lo que representa más del 58,58 % de su capacidad instalada de energía renovable (excluida la gran energía hidroeléctrica). Entre ellas, las instalaciones solares montadas en suelo representaron 69,19 GW y otros 2,59 GW procedieron de paneles solares híbridos.. En las zonas rurales con suministro eléctrico limitado, las instalaciones fuera de la red, como linternas solares y microrredes, totalizaron 3,76 GW.
Con el continuo aumento de la capacidad instalada, la energía fotovoltaica india se ha convertido en una fuerza importante en el mercado fotovoltaico mundial.
Similar a esto es Vietnam. Como economía emergente en el Sudeste Asiático, Vietnam ha experimentado un rápido desarrollo económico, una industrialización y urbanización aceleradas en los últimos años, y la demanda de electricidad también ha aumentado en consecuencia. Los datos públicos muestran que la demanda de electricidad de Vietnam está aumentando a una tasa anual del 10-12%. Por lo tanto, el gobierno vietnamita introduce activamente capital y tecnología extranjeros para promover el desarrollo de la industria fotovoltaica.
Vale la pena señalar que las empresas fotovoltaicas chinas ocupan una posición importante en el mercado vietnamita y han emprendido una serie de proyectos de centrales fotovoltaicas a gran escala. Por ejemplo, la central solar de Youting en Vietnam es la central de energía solar más grande del sudeste asiático realizada por China Power Construction Group. El proyecto tiene una capacidad instalada de casi 500 megavatios, lo que proporciona un fuerte apoyo al suministro de energía de Vietnam.
Echemos un vistazo a los países en desarrollo de América Latina como Brasil, Argentina y México. El suministro de energía de estos países depende principalmente de la energía hidroeléctrica, pero en los últimos años, con el aumento de los extremos climáticos globales, especialmente la sequía causada por el fenómeno de El Niño, la energía hidroeléctrica se ha visto gravemente afectada, lo que ha resultado en un suministro de energía inestable y obstáculos importantes para el desarrollo regional. desarrollo económico.
Según los últimos informes, Argentina ha adoptado cortes de energía planificados en respuesta al aumento en el consumo de electricidad de aire acondicionado. La sequía en Brasil también es grave: afecta aproximadamente al 59% del país y provoca una escasez de suministro de energía.
Para resolver este dilema, estos países han recurrido al campo de las nuevas energías, especialmente la generación de energía fotovoltaica, y gradualmente han mostrado un gran potencial de desarrollo.
Los datos muestran que en 2023, la capacidad instalada de energía fotovoltaica en América Latina alcanzó un récord, con la nueva capacidad saltando a 21 gigavatios, y se espera que aumente aún más a 23 gigavatios en 2024. Entre ellos, la demanda La demanda de energía fotovoltaica en Brasil, Chile y México continúa aumentando, convirtiéndose en el foco de la inversión mundial en la industria fotovoltaica.
Brasil ha tenido un desempeño particularmente bueno en esta transformación. Su nueva versión del "Plan de Crecimiento Acelerado" se centra en el desarrollo de la energía fotovoltaica y eólica, especialmente el establecimiento de nuevos proyectos de generación de energía fotovoltaica en la región noreste. En 2023, la nueva capacidad fotovoltaica instalada de Brasil aumentará en 7 GW, y la capacidad instalada total ascenderá a 44 GW, lo que representa el 18,9% de su suministro eléctrico total.
1.2. Beneficios económicos de la industria fotovoltaica
El desarrollo de la industria fotovoltaica no sólo favorece la solución del problema de la escasez de energía en los países en desarrollo, sino que también impulsa el desarrollo de cadenas industriales relacionadas. Dado que la construcción y operación de centrales fotovoltaicas requiere mucha mano de obra, recursos materiales y financieros, puede impulsar el desarrollo de múltiples industrias, como la manufactura, la construcción y los servicios financieros. Al mismo tiempo, la operación y el mantenimiento de centrales fotovoltaicas también requieren un gran número de profesionales, lo que proporciona un gran número de oportunidades de empleo para el área local.
Tomando a la India como ejemplo, el gobierno ha atraído a un gran número de empresas nacionales y extranjeras para que ingresen al mercado fotovoltaico indio ofreciendo políticas favorables como incentivos fiscales y subsidios, lo que ha promovido el rápido desarrollo de la industria fotovoltaica. Según datos de la Asociación India de Energía Solar, la industria fotovoltaica de la India se ha convertido en una de las industrias más prometedoras del país, haciendo importantes contribuciones al crecimiento económico y la creación de empleo.
1.3. Perspectivas futuras
Bajo la transformación acelerada de la energía global y la necesidad de mejorar el desarrollo económico, la industria fotovoltaica en los países en desarrollo todavía tiene un espacio muy amplio para el desarrollo. Se espera que se siga aumentando el apoyo político para promover la innovación tecnológica y la modernización industrial en la industria fotovoltaica y acelerar la reducción de los costos de generación de energía fotovoltaica.
Sin embargo, también es necesario ver que para la mayoría de los países en desarrollo, la popularización y aplicación de la generación de energía fotovoltaica aún deben superar muchas dificultades. Por ejemplo, el problema de financiación de los proyectos fotovoltaicos sigue siendo una limitación importante, y la falta de construcción de redes y de tecnología de almacenamiento de energía también constituye un obstáculo para la producción efectiva de energía fotovoltaica.
Vale la pena señalar que con la creciente participación de empresas chinas en la cadena industrial de energía verde, la relación de cooperación entre China y los países en desarrollo de América Latina y la vecina se está profundizando. Según el análisis de la Agencia Brasileña de Promoción de Exportaciones e Inversiones, se espera que la cooperación con empresas chinas promueva la transformación energética en América Latina y promueva los intercambios de tecnología y las entradas de capital.
2. El mercado de "seguridad energética fotovoltaica" en algunos países desarrollados, incluida Europa
2.1. Seguridad Energética y Autosuficiencia
Para los países desarrollados, como Europa, la seguridad energética es una piedra angular importante para mantener la seguridad nacional y el desarrollo económico.
En los últimos años, con los cambios en el panorama energético global y el aumento de los riesgos geopolíticos, los países europeos se han vuelto cada vez más conscientes de la importancia de la autosuficiencia energética. La industria fotovoltaica, con sus características limpias y renovables, se ha convertido en una forma importante para que los países europeos logren la transformación de la estructura energética y garanticen la seguridad energética.
Tomemos como ejemplo a Alemania, líder de la industria fotovoltaica europea. En los últimos años, el mercado fotovoltaico alemán se ha desarrollado rápidamente y ha madurado. El gobierno local alienta a los residentes y empresas a instalar sistemas fotovoltaicos mediante subsidios, préstamos preferenciales e incentivos fiscales.
Especialmente para la energía fotovoltaica para balcones, Alemania es el mercado más grande de Europa para la energía fotovoltaica para balcones y su posición de liderazgo es estable.
Se entiende que en los días soleados, los sistemas fotovoltaicos de balcón pueden satisfacer la mayor parte de las necesidades eléctricas de los hogares normales de dos personas en Alemania. En períodos de fuertes aumentos en los precios de la energía, los equipos fotovoltaicos pequeños y fáciles de instalar pueden recuperar sus costos en aproximadamente 2 a 4 años.
Según datos de las agencias estadísticas pertinentes, Alemania tendrá 220.000 nuevas capacidades instaladas de sistemas fotovoltaicos enchufables para balcones en el primer semestre de 2024, alcanzando los 200 MW. La capacidad instalada en el segundo trimestre se triplicó en comparación con el primer trimestre, y la capacidad total registrada promedio aumentó de 800 W el año pasado a alrededor de 900 W este año.
Echemos un vistazo a Francia. Como una de las economías más importantes de Europa, la estructura energética de Francia es principalmente la energía nuclear. Sin embargo, en los últimos años, el gobierno francés también ha comenzado a prestar atención al desarrollo de energías renovables como la fotovoltaica, y ha formulado una serie de estrategias de transformación y políticas de apoyo para promover el desarrollo de la industria fotovoltaica.
En la actualidad, el mercado fotovoltaico francés se encuentra en una etapa de rápido desarrollo y se espera que mantenga una tendencia de alto crecimiento en los próximos años.
2.2. El auge de la energía fotovoltaica agrícola
Vale la pena señalar que en los últimos años, los países europeos todavía están explorando el modelo de desarrollo de la energía fotovoltaica agrícola.
Por ejemplo, como potencia agrícola de renombre mundial, los Países Bajos han estado promoviendo activamente la implementación de proyectos fotovoltaicos agrícolas, alentando a los agricultores a instalar paneles fotovoltaicos sobre las tierras de cultivo mediante apoyo político y subsidios financieros. Estos paneles fotovoltaicos no solo proporcionan efectos de sombra para las tierras agrícolas, reducen la evaporación del agua y el uso de pesticidas, sino que también utilizan energía solar para generar electricidad, lo que brinda beneficios económicos adicionales a los agricultores.
Además, los proyectos agrícolas fotovoltaicos en los Países Bajos también se centran en conectarse con redes inteligentes, lograr un despacho y almacenamiento flexibles de electricidad y mejorar la estabilidad y confiabilidad del sistema eléctrico.
2.3. Perspectivas futuras
Las políticas favorables siguen impulsando la demanda de energía fotovoltaica para balcones en Europa.
Los datos muestran que Alemania tiene actualmente una población de más de 83 millones, incluidos más de 40 millones de hogares. Una encuesta realizada por una institución profesional mostró que el 69% de los propietarios elegibles tienen la intención de instalar sistemas fotovoltaicos domésticos, y el 16% de los propietarios tienen previsto instalarlos durante el próximo año. Se puede ver que se acaba de abrir el espacio para la instalación de sistemas fotovoltaicos domésticos en Alemania.
Es particularmente digno de mención que el 4 de julio, la cámara baja del Parlamento alemán aprobó una enmienda legislativa que permite a los propietarios e inquilinos de apartamentos instalar sistemas de generación de energía solar en sus balcones, que los propietarios o las asociaciones de propietarios no pueden impedir sin razones legítimas. . En Alemania, la proporción de inquilinos se acerca a la mitad de la población total. Ahora el nuevo proyecto de ley protege los derechos de los inquilinos a utilizar sistemas fotovoltaicos en balcones y está llegando un enorme grupo de usuarios.
Al mismo tiempo, el gobierno alemán también se ha fijado el objetivo de instalar sistemas fotovoltaicos de 215 GW para 2030, lo que requiere un aumento de 22 GW de sistemas fotovoltaicos cada año.
Además, el auge de modelos emergentes como la energía fotovoltaica agrícola también traerá nuevos puntos de crecimiento al mercado fotovoltaico europeo.
3. El mercado de "aplicaciones especiales fotovoltaicas" representado por áreas sin electricidad debido a la guerra, etc.
3.1. Escasez de energía en el contexto de la guerra
Los conflictos y guerras en Rusia, Ucrania, Palestina e Israel han provocado una grave escasez de energía. La infraestructura en estas áreas puede sufrir graves daños y las interrupciones del suministro eléctrico se han convertido en la norma. En áreas con sistemas eléctricos imperfectos, las aplicaciones fotovoltaicas especiales representadas por las microrredes fotovoltaicas son particularmente importantes.
La microrred fotovoltaica se refiere a un sistema de energía independiente compuesto por centrales fotovoltaicas, sistemas de almacenamiento de energía, sistemas de distribución y cargas de energía. Puede implementarse y ponerse en funcionamiento rápidamente en poco tiempo sin el apoyo de una gran red eléctrica, proporcionando a los residentes locales un suministro de energía estable.
Las ventajas de las microrredes fotovoltaicas son su conexión en red independiente y sus características de implementación flexible, que pueden responder rápidamente a los cambios en la demanda de energía en poco tiempo. Al mismo tiempo, las microrredes fotovoltaicas también se pueden combinar con sistemas de energía tradicionales para formar un modo de suministro de energía complementario y mejorar la estabilidad y confiabilidad del sistema de energía.
Se entiende que en 2024, en los mercados de Ucrania y Gaza, las microrredes de almacenamiento fotovoltaico se convertirán en la primera opción para los residentes en guerra.
En algunas zonas de conflicto de Ucrania, el sistema tradicional de suministro de energía ha sido destruido y las interrupciones del suministro se han convertido en la norma. Para garantizar las necesidades básicas de los residentes locales, el área local proporciona suministro de energía de emergencia a los residentes locales mediante la instalación de estaciones de energía fotovoltaica portátiles y estaciones de carga solar.
El 24 de julio de este año, cuando el Ministro de Asuntos Exteriores de Ucrania visitó China, invitó específicamente a las empresas chinas a fortalecer la cooperación con Ucrania en el campo de las energías renovables. Según las estadísticas de Kaiyuandianxin, el déficit energético de Ucrania en invierno es de unos 6 GW, pero si las instalaciones de calefacción se ven afectadas y aumenta el uso de energía distribuida, la demanda de energía renovable de Ucrania será aún mayor.
Debido al impacto a largo plazo de la guerra y el conflicto en la región palestina, el suministro de energía es inestable y el precio alto. Se pueden ver farolas solares, calentadores de agua solares y otros equipos por todas partes, proporcionando soluciones de energía limpia y barata para los residentes locales.
En Gaza, donde el conflicto es más intenso, la energía fotovoltaica también se está convirtiendo en una de las principales formas de suministro de energía. La gente utiliza la energía fotovoltaica para resolver la mayoría de sus necesidades energéticas. Incluso si son atacados por el ejército israelí, pueden reconstruirse rápidamente.
3.2. Desafíos y soluciones
Sin embargo, en el desarrollo del mercado de aplicaciones especiales fotovoltaicas, también existen algunos desafíos.
En primer lugar, las zonas sin electricidad suelen tener una infraestructura débil y sistemas imperfectos de transmisión y distribución de energía, lo que trae ciertas dificultades a la construcción y operación de centrales fotovoltaicas.
En segundo lugar, estas regiones suelen estar económicamente atrasadas, con bajos niveles de ingresos y un poder adquisitivo y una capacidad de pago limitados para los productos fotovoltaicos.
Para superar estos desafíos, es necesario tomar una serie de medidas. Por ejemplo, a través de la asistencia gubernamental y la cooperación internacional, se debe proporcionar a estas regiones la construcción de la infraestructura necesaria y el apoyo financiero.